lv strain ecg | ecg voltage criteria for lvh lv strain ecg R Wave Peak Time Rwpt - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG . Product Description. This connector can be connected to headers having 2.36mm diameter pins. *The mating section of the contact has a triangular configuration so that the terminal grips the round mating pin at three points. *One position has a different pitch than the others. Pitch. 8.0 mm. Current Rating.
0 · what is lvh on ecg
1 · my LVHN sign in
2 · lvh with strain pattern meaning
3 · lvh signs on ecg
4 · left ventricular hypertrophy on ecg
5 · ecg voltage criteria for lvh
6 · ecg findings in lvh
7 · criteria for lvh on ecg
52 talking about this
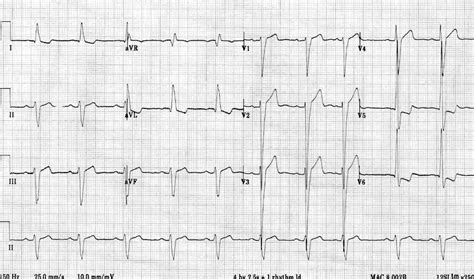
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST .R Wave Peak Time Rwpt - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG .ECG Pearl. There are no universally accepted criteria for diagnosing RVH in .ECG Criteria for Left Atrial Enlargement. LAE produces a broad, bifid P wave in .
In LBBB, conduction delay means that impulses travel first via the right bundle .
U Waves - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
Left Axis Deviation - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG .
Learn how to interpret ECG changes in LVH, such as large R-waves in left-sided leads and secondary ST-T changes. Find out the causes, indexes and . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a .
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) MRI. Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. It may include medicines, catheter procedures or surgery. It's important .Electrocardiographic (ECG) left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) with strain pattern is said to be present when, apart from the voltage criterion for ECG-LVH, there is also a downsloping .
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6.
ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and deep S-waves in right-sided chest leads (V1, V2). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) MRI. Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. It may include medicines, catheter procedures or surgery. It's important to manage conditions such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea, which can cause blood pressure to be higher. Medications.
Electrocardiographic (ECG) left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) with strain pattern is said to be present when, apart from the voltage criterion for ECG-LVH, there is also a downsloping asymmetrical ST-segment depression with inverted asymmetric T wave ≥ 0.1 mV opposite the QRS axis in a resting ECG.Left ventricular hypertrophy can be diagnosed on ECG with good specificity. When the myocardium is hypertrophied, there is a larger mass of myocardium for electrical activation to pass. What is LVH? When the left ventricle is constantly pumping against increased resistance (chronically high blood pressure, aortic stenosis), the muscle hypertrophies like any other muscle. The thickened muscle wall takes longer to depolarize and longer to repolarize.
Conventional assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) using the electrocardiogram (ECG), for example, by the Sokolow–Lyon, Romhilt–Estes or Cornell criteria, have relied on assessing changes in the amplitude and/or duration of the QRS complex of the ECG to quantify LV mass. The ECG diagnosis of LVH is predominantly based on the QRS voltage criteria. The classical paradigm postulates that the increased left ventricular mass generates a stronger electrical field, increasing the leftward and posterior QRS forces, reflected in . LV strain is most commonly seen in one or more leads that look at the left ventricle (leads I, aVL, V4, V5, V6); less commonly it can be seen in inferior leads. If a strain equivalent pattern occurs in association with voltage for LVH, specificity for true LVH is greatly enhanced compared to the voltage criteria alone. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6.
ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and deep S-waves in right-sided chest leads (V1, V2). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) MRI. Treatment for left ventricular hypertrophy depends on the cause. It may include medicines, catheter procedures or surgery. It's important to manage conditions such as high blood pressure and sleep apnea, which can cause blood pressure to be higher. Medications.Electrocardiographic (ECG) left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) with strain pattern is said to be present when, apart from the voltage criterion for ECG-LVH, there is also a downsloping asymmetrical ST-segment depression with inverted asymmetric T wave ≥ 0.1 mV opposite the QRS axis in a resting ECG.
Left ventricular hypertrophy can be diagnosed on ECG with good specificity. When the myocardium is hypertrophied, there is a larger mass of myocardium for electrical activation to pass. What is LVH? When the left ventricle is constantly pumping against increased resistance (chronically high blood pressure, aortic stenosis), the muscle hypertrophies like any other muscle. The thickened muscle wall takes longer to depolarize and longer to repolarize.
Conventional assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) using the electrocardiogram (ECG), for example, by the Sokolow–Lyon, Romhilt–Estes or Cornell criteria, have relied on assessing changes in the amplitude and/or duration of the QRS complex of the ECG to quantify LV mass.
The ECG diagnosis of LVH is predominantly based on the QRS voltage criteria. The classical paradigm postulates that the increased left ventricular mass generates a stronger electrical field, increasing the leftward and posterior QRS forces, reflected in .
burberry x comme des carcon
How Many Pounds in a Gram? 1 Gram is equal to 0.002204622476038 Pounds. 1 g = 0.002204622476038 lbs. Grams to Pounds Conversions. 500 g = 1.102311 lbs. 100 g = 0.220462 lbs. 200 g = 0.440924 lbs. 300 g = 0.661387 lbs. 1000 g = 2.204622 lbs. 400 g = 0.881849 lbs. 250 g = 0.551156 lbs. 0 g = 0 lbs. 700 g = 1.543236 lbs. 800 g = 1.763698 .
lv strain ecg|ecg voltage criteria for lvh